From Manual to Automated: A Practical Beginner’s Roadmap to Algo Trading in India

Introduction
Algorithmic trading has shaped global financial markets for decades. What was once the exclusive domain of institutional desks and high-frequency firms is now accessible to retail traders in India. With modern APIs, no-code strategy builders, VPS hosting, and SEBI-backed regulatory clarity, retail traders can automate every part of their trading workflow.
However, many traders still depend on manual chart-watching, discretionary decisions, and emotionally driven entries and exits. This leads to inconsistent performance, fatigue, and missed opportunities. Algo trading solves these problems through data-driven logic, consistent execution, and reliable automation.
This guide presents a complete, structured roadmap to help beginners transition from manual to automated trading using retail-friendly platforms and tools available in India.
Why Manual Trading Often Fails Retail Traders
Emotional Decisions
Fear of loss, greed, panic during volatility, and hesitation make manual trading unpredictable. Algo trading replaces emotion with fixed rules.
Delayed Execution
Human reaction time is slow. By the time a trader identifies a breakout or breakdown, the price usually moves ahead. Algorithms react instantly to predefined signals.
Limited Capacity
A human can track only a handful of charts at a time. Algorithms can monitor hundreds of instruments simultaneously across multiple timeframes.
Fatigue and Inconsistency
Continuous screen-watching for hours impacts judgment, discipline, and decision quality. Algorithms do not experience burnout.
Lost Time
Manual trading consumes hours that could otherwise be spent on professional work, research, or personal commitments.
Algorithmic trading solves these limitations by delivering precision, consistency, and speed.
Part 1: Understanding the Basics of Algo Trading
What Is Algorithmic Trading?
Algorithmic trading refers to the automated execution of buy or sell orders based on pre-programmed logic. When market conditions satisfy the algorithm’s rules, it executes trades automatically through a broker API or a platform.
Simple examples include:
- Buy when the 20-day EMA crosses above the 50-day EMA.
- Exit when the price falls 1.5 percent from the entry price.
- Do not trade during the first 15 minutes after market open.
- Close all positions before 3:25 PM.
The advantage lies in executing these rules consistently and without emotional bias.
Key Concepts to Learn
Trading Instruments
Retail algo traders in India commonly automate:
- Equity (stocks)
- Futures and Options
- Currency pairs
- Commodities
- Crypto (offshore platforms)
Beginners should start with stocks due to simplicity and lower leverage.
Order Types
Your algorithm must understand how orders are placed:
- Market orders
- Limit orders
- Stop-loss orders
- Trailing stop-loss orders
Risk Management Essentials
Your strategy must define:
- Maximum risk per trade (1–2 percent recommended)
- Stop-loss distance
- Maximum daily loss limit
- Maximum drawdown allowed
- Position sizing formula
- Avoiding excessive leverage
Without risk controls, even a great strategy can fail.
Part 2: The 9-Step Beginner Roadmap to Algo Trading
Step 1: Build Your Foundation (Weeks 1–2)
Spend time learning:
- Market fundamentals
- Technical analysis basics
- Position sizing and risk frameworks
Recommended milestone: Be able to explain moving averages, support–resistance, slippage, and why stop-losses matter.
Step 2: Select Your Asset Class (Week 2–3)
Focus on just one for the first few months.
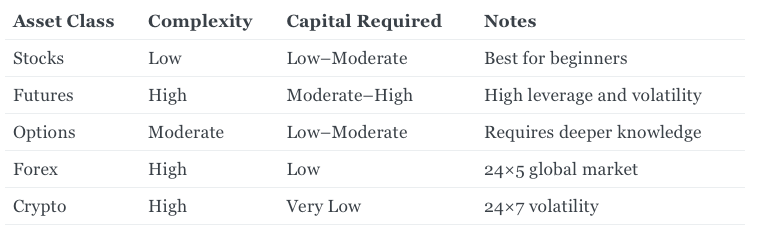
Most Indian beginners achieve the fastest progress starting with stocks.
Step 3: Choose an Algo Trading Platform (Week 3–4)
Evaluate platforms based on:
- Backtesting capability
- Paper trading support
- Strategy builder interface
- Connection stability
- Broker integrations
- Cost structure
Popular platforms for Indian retail traders include:
- Zerodha Streak (no-code)
- Tradetron (no-code + advanced logic)
- Upstox Algo Lab (API-driven)
- Angelone Smart API
Beginners should start with Streak or Tradetron to gain confidence before moving to coding-based systems.
Step 4: Learn Programming (Optional but Beneficial) (Weeks 4–8)
Coding is not mandatory, but learning Python provides full control over logic, custom indicators, and API interactions.
A simple learning plan:
- Week 1: Python basics
- Week 2: pandas and numpy
- Week 3: Backtesting with Backtrader or VectorBT
- Week 4: Connecting to broker APIs
Time investment: 40–60 hours.
If coding is not your preference, you can continue using no-code tools or hire freelance developers.
Step 5: Build Your First Strategy (Weeks 8–10)
Start with a simple, robust, rule-based system.
Example Beginner Strategy: EMA Crossover
- Buy when 10-EMA crosses above 50-EMA
- Sell when 10-EMA crosses below 50-EMA
- Stop-loss: 2–3 percent
- Risk: 2 percent per trade
- Avoid low-volume hours
- Close positions at end of day if following intraday approach
Alternative starter strategies:
- RSI-based mean reversion
- Breakout trading
- Trend-following systems
- Momentum-based entries
Avoid creating overly complex systems with too many indicators. Complexity increases curve-fitting risk.
Step 6: Backtest the Strategy (Weeks 10–12)
Backtesting helps identify performance across different market conditions.
Key performance metrics:
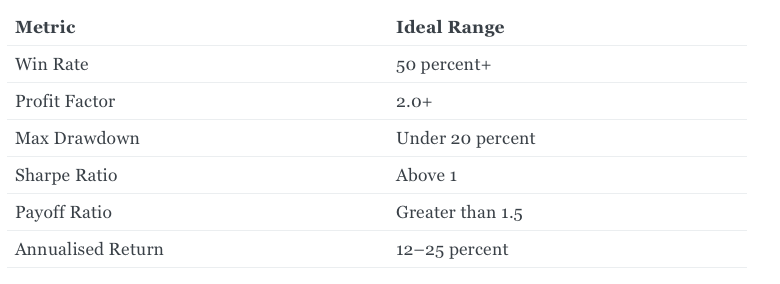
Always include brokerage, STT, exchange fees, GST, slippage, and impact cost in your backtests.
Use multi-year data covering bull, bear, and sideways markets.
Conduct:
- In-sample tests
- Out-of-sample validation
- Walk-forward testing
Choose robustness over peak performance.
Step 7: Paper Trade in Live Conditions (Weeks 12–14)
Paper trading replicates real-time conditions without risking actual capital.
During this phase, verify:
- Correct order execution
- Accurate position sizing
- Realistic slippage behaviour
- API stability
- Strategy behaviour under volatility
Paper trading for at least four weeks is recommended, ideally eight for confidence.
Step 8: Set Up Your Broker API (Week 14)
Choose a SEBI-compliant broker that supports retail algo trading:
- Zerodha
- Angelone
- Upstox
- 5paisa
Process includes:
- Open trading and demat account
- Complete KYC
- Request API access
- Secure API key & API secret
- Configure static IP if required
- Test API connectivity
Follow strong security practices such as two-factor authentication and secure storage for API keys.
Step 9: Go Live with Caution (Week 15+)
Adopt a phased deployment approach:
Phase 1 (Weeks 1–4)
- Deploy 10–20 percent of your planned capital
- Monitor every day
Phase 2 (Weeks 5–12)
- Increase to 50 percent
- Evaluate real-world slippage, latency, and behaviour
Phase 3 (After Week 12)
- Deploy full capital
- Monitor weekly instead of daily
Remember: Live trading results rarely match backtests exactly. Slippage and costs affect returns.
Part 3: Common Mistakes New Algo Traders Make
Over-Optimising
Excessive parameter tuning makes the model fit historical noise rather than underlying patterns. This leads to poor live performance.
Ignoring Costs
If you ignore slippage, taxes, and brokerage, your backtested profit can disappear in real trading.
Weak Risk Management
Proper stop-loss, capital allocation, and drawdown controls are crucial.
Complex Strategies
Simple strategies are surprisingly resilient. Complexity does not guarantee performance.
Not Monitoring the Algorithm
Even automated systems require periodic reviews. Technology, APIs, and market conditions change.
Part 4: SEBI Regulations for Retail Algo Trading (India)
In recent years, SEBI and NSE have implemented clear guidelines to safeguard retail traders and ensure standardised practices for API-based trading.
Key regulatory elements include:
- Static IP requirement for algorithmic order routing
- Order tagging and proper audit trails
- Broker approval for algorithms
- Strict API order rate limits
- Monitoring obligations for brokers
For a comprehensive breakdown of the 2025 regulatory changes, refer to the official Fintrens guide:
NSE Retail Algo Trading Rules (Nov 2025): Static IP, Order Tagging and Compliance Guide
https://blogs.fintrens.com/nse-retail-algo-trading-rules-nov-2025-static-ip-order-tagging-compliance-guide/
This reference explains the compliance framework for retail algo traders in detail.
Part 5: Setting Realistic Expectations
Capital Requirements
- Minimum: ₹25,000–₹50,000
- Ideal: ₹2–5 lakh
Start with small capital and scale up gradually.
Expected Returns
- Conservative: 8–15 percent
- Moderate: 15–25 percent
- High-risk: 25–40 percent (with volatility)
Be cautious of unrealistic promises. Markets do not guarantee fixed returns.
Learning Timeline
- Months 1–2: Core learning
- Months 3–4: Strategy creation and testing
- Months 5–6: Paper trading
- Month 7 onwards: Live trading with small capital
- Year 1–2: Continuous improvement
Algo trading is a long-term skill.
Part 6: A Typical Day in the Life of an Algo Trader
A realistic daily workflow:
- Morning: Review overnight global news, confirm API connection, check brokerage funds
- Market Hours: Algorithm executes trades; trader monitors occasionally
- Afternoon: Review performance, validate logs, cross-check any anomalies
- End of Day: Export metrics, analyse deviations, make notes for the next session
Algo trading is designed to be structured, predictable, and consistent.
Part 7: Troubleshooting and Future Strategy Development
If your live trading results diverge from expectations:
- Remain calm
- Check whether market conditions changed
- Validate execution logs
- Analyse slippage patterns
- Inspect API connectivity
- Temporarily pause and return to paper trading if required
Once your first system becomes stable:
- Optimise parameters
- Add diversification through additional uncorrelated strategies
- Test new timeframes or instruments
- Explore machine learning and sentiment data
- Expand into multi-strategy portfolios
Evolution is a continuous part of algorithmic trading.
Part 8: Recommended Learning Resources
Books
- Algorithmic Trading by Ernest Chan
- Trading and Exchanges by Larry Harris
- A Random Walk Down Wall Street by Burton Malkiel
Platforms
- QuantInsti
- TradingView
- Coursera
- Investopedia
- Firefly By Fintrens
Tools
- Backtrader
- Zipline
- VectorBT
- Pandas and NumPy
These help build strong foundations and deepen practical understanding.
Conclusion
You now have a complete, actionable roadmap to begin your journey as an algo trader in India. The transition from manual to automated trading requires patience, structured learning, and disciplined execution. It is not about building the most complex model, but about creating a reliable system that runs consistently.
Your roadmap:
This Week
- Select your asset class
- Choose a trading platform
- Begin foundational learning
Next Four Weeks
- Build a simple strategy
- Backtest thoroughly
Next Eight Weeks
- Paper trade
- Set up your broker API
- Start small in live trading
Algo trading rewards learners who embrace data, discipline, and continuous improvement. Your first automated trade is the starting point toward building a scalable and reliable trading framework.
Further Reading on SEBI Retail Algo Regulations
NSE Retail Algo Trading Rules (Nov 2025): Static IP, Order Tagging and Compliance Guide
https://blogs.fintrens.com/nse-retail-algo-trading-rules-nov-2025-static-ip-order-tagging-compliance-guide/
Additional Fintrens Resources
Official Website
Firefly Documentation
https://docs.firefly.fintrens.com
Join the Fintrens WhatsApp Channel
https://whatsapp.com/channel/0029VackYjRLdQegrpD4uj2T